16 minutes to read
What is stress testing in software development?


Chief Technology Officer
QA stress testing is an integral part of the development process for any application. According to a recent study, the number of downloads for mobile apps alone worldwide is forecast to experience significant growth in all segments in 2027, with the Games segment achieving the highest value of 176.1 billion downloads. Along with the popularity of custom software, websites, SaaS and AI products, user expectations are also on the rise and your product must be able to meet them.
What is a stress test? It is a crucial pre-launch check that helps evaluate how well your project performs under extreme conditions and large loads of data. Neglecting proper stress testing can lead to lost revenue, critical system vulnerabilities, and overall customer dissatisfaction: a 2024 survey by Sauce Labs claims that 40% of users are less likely to return to a website or an application after a bad experience.
Stress testing can help you identify performance limits, detect issues and vulnerabilities, and ensure the proper functionality of your product under extreme conditions. So, what differs stress testing among all software testing services, and why does your app need it?
Why is stress testing important?
When unexpected circumstances occur, it gradually becomes difficult to estimate how the software will behave and respond. In this regard, traditional testing is rather limiting. Even if developers refine and optimize their code, they can still only theorize about the consequences of high data loads on the software’s performance.
Stress test your app's limits before your users do
Imagine a scenario where a healthcare company launches a new telehealth platform aimed at connecting patients with doctors for online consultations. On launch day, there’s an overwhelming surge of users, as thousands of patients log on simultaneously to access care.
This sudden increase in traffic can lead to slow loading times and even system crashes, leaving many patients unable to schedule appointments or receive timely medical advice. In the long run, this can result in patient frustration, an influx of negative feedback, and significant damage to the company’s reputation in a critical industry where trust and reliability are paramount.
To avoid this, developers must resort to software testing services that allow simulating high user activity before launch. In this way, developers will make sure that the servers can handle high traffic and maintain smooth gameplay without lags or crashes, thus preserving the company’s reputation and brand image.
Types of stress testing
Stress testing is a vital component of preparing your project for global launch. It is commonly applied in finance, software engineering, and healthcare. There are several types of testing that will help you make sure that your solution is reliable.
Load testing
Among all the types of stress tests, load testing is especially relevant for apps designed to process large loads of data and perform under expected (and, often, unexpected) load conditions. A load check can simulate user traffic to see if your app can handle expected loads of data and not crash.
Volume testing
Volume testing allows you to check how an app handles large amounts of data. It tests the app’s performance in the following way: it increases the size of the database or the amount of input data to detect any possible inconsistencies or capacity issues.
Application testing
Application testing helps developers ensure that the app meets its functional and non-functional requirements. It includes checking usability, performance, security, and compatibility. Application testing is integral if you want to deliver a reliable and user-friendly product.
Transactional testing
In transactional testing, developers focus on the accuracy and performance of critical transactions. For example, logging into an account or completing a payment. Transactional tests help ensure that these operations work correctly under normal and high loads.
Distributed testing
Distributed testing is used to test apps deployed across multiple servers or locations. It checks how the app performs in a distributed environment. Distributed testing ensures seamless interactions and communication between different components of your product.
Systemic testing
In systemic testing, evaluation of the entire system as a whole is allowed, including hardware, software, and network components. The aim of this check is to ensure all parts work together correctly and meet the system’s overall requirements.
Exploratory testing
Lastly, exploratory testing is an informal, flexible approach where testers actively explore the app without predefined scripts. It’s used to uncover unexpected issues and improve understanding of how the app behaves in various scenarios.
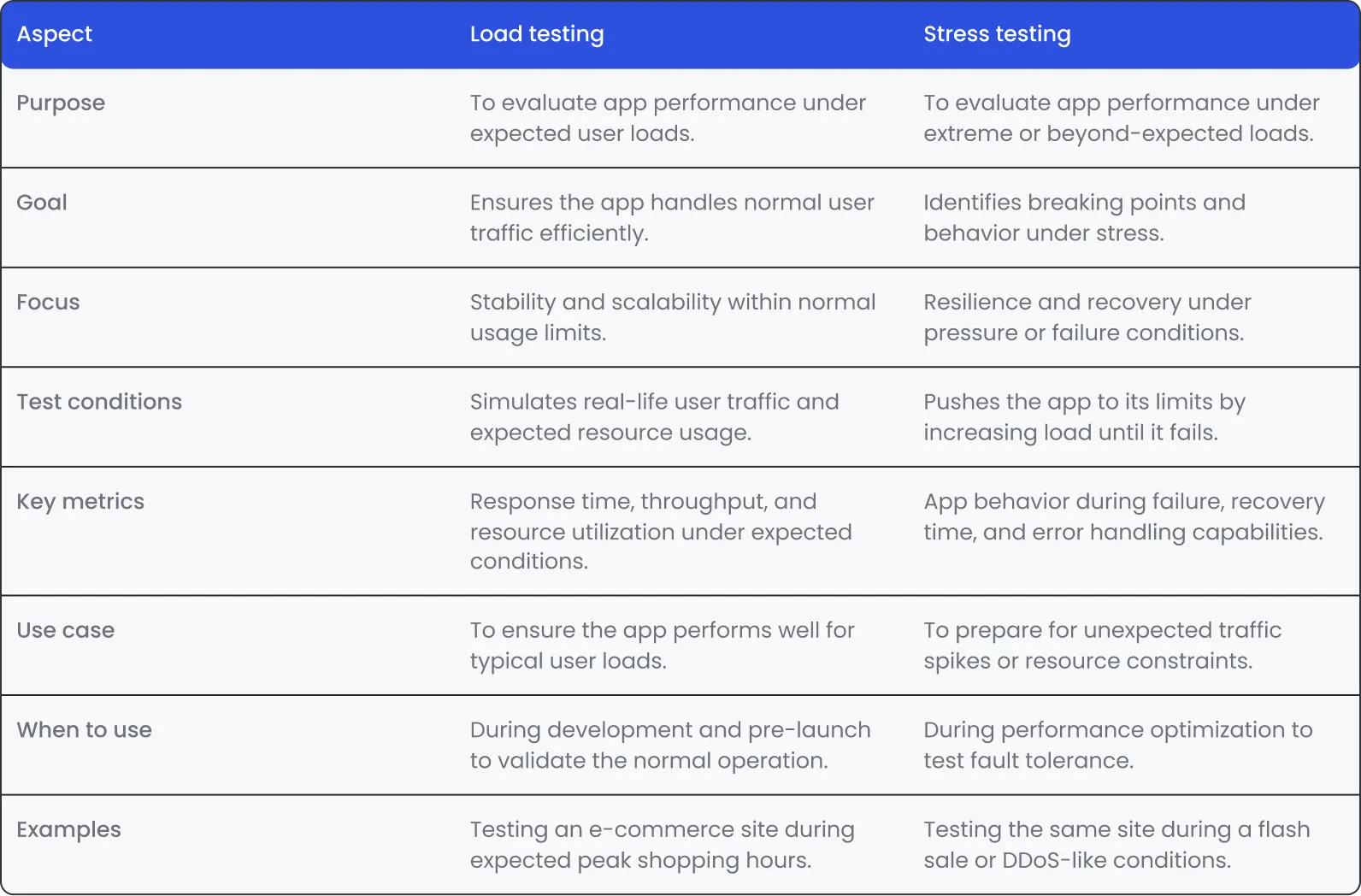
Load testing vs. stress testing
Load and stress testing services might seem similar but in fact, these are two separate qa tests suited for different purposes in the development process.

Сomparison of load and stress testing aspects.
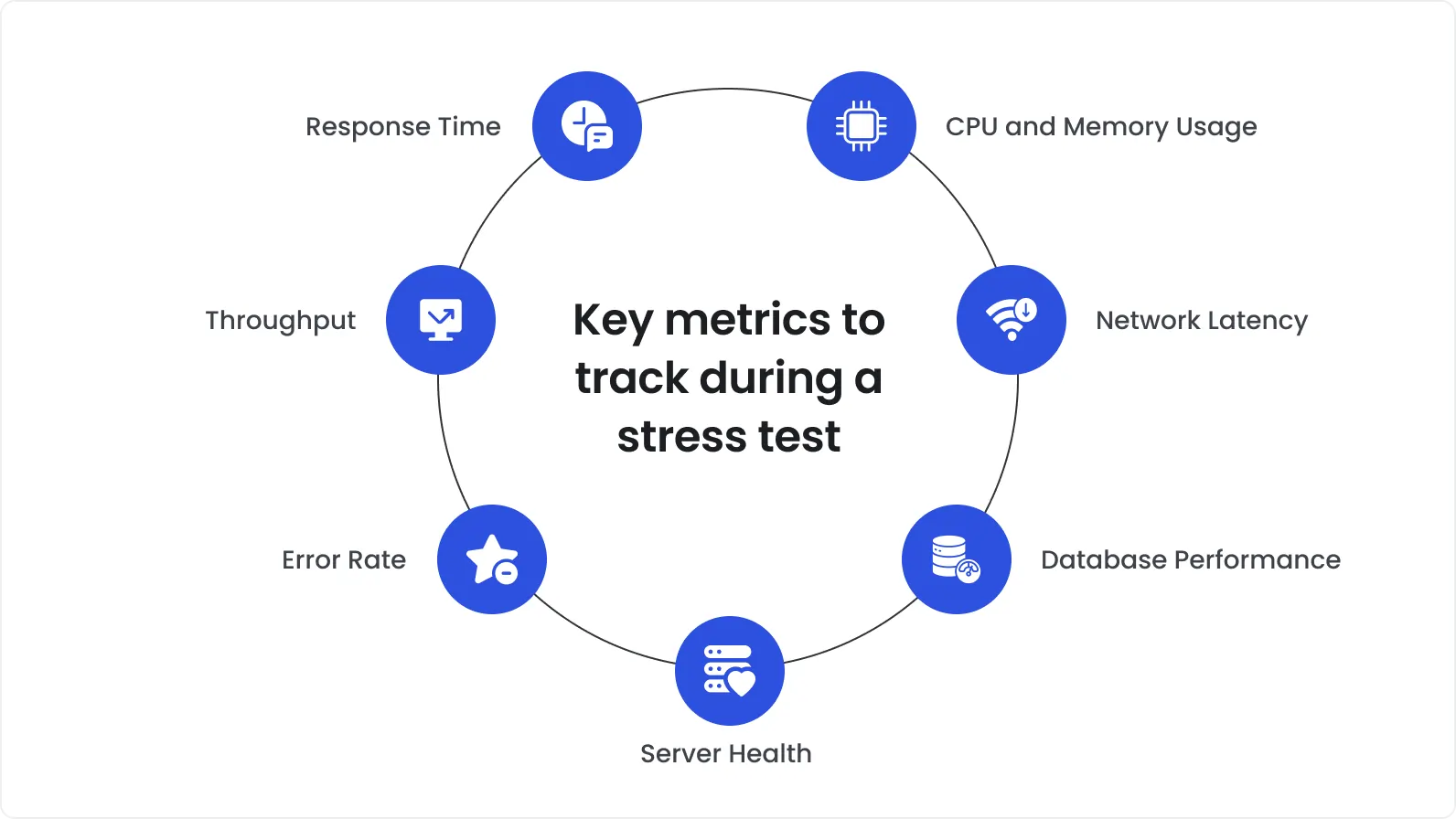
Metrics used for stress testing
Stress testing is a complex process that consists of many steps and layers. However, once you get the knack of it and build your own stress test algorithm according to all the recommendations, stress testing your app will turn into a smooth and relatively fast procedure. Below, we will explain the key metrics you need to evaluate for proper stress testing of your application.
Measuring system scalability and performance
Scalability determines how well your app can handle the increased load of data and requests. Performance, in turn, measures how quickly and effectively the system responds under different loads. During stress tests, a developer evaluates both. How? By pushing the system beyond its normal limits. Then, it is possible to retrieve such key metrics as response times, throughout, and error rates. In this way, you can detect possible weaknesses in the system and get rid of them early on, thus optimizing performance and ensuring usability even during unexpected spikes in data loads.
Pages per Second
Pages per Second is a metric that helps you measure how many web pages the system serves per second under stress. If you see a high value, it means that the system can handle more user requests efficiently. If you notice a drop in pages per second, especially a significant and unexpected one, during a stress test, it likely means that the system is degrading. If you monitor this metric adequately, you will identify server-related issues on time, for example, slow database queries or overloaded servers. In this way, you will ensure that the system can remain usable under heavy traffic.
Throughput
Throughput measures how much data the system processes within a specific timeframe; most often, it’s done in kilobytes or megabytes per second. It helps you see how efficiently the app handles user requests and responses during stressful situations. If you spot a sudden drop in throughput under heavy loads, you can indicate the weaknesses and limitations in the network and hardware. To maintain high throughput even under extreme conditions, you can optimize the use of bandwidth and server hardware.
Rounds
Rounds help you track the total number of checks that you complete during a stress test. Each round is a set of user actions or requests users make to the system. If you track rounds, you are able to ensure that your test covers different scenarios, including peak and failure conditions. If you spot a decrease in completed rounds with the increase in the load, it’s likely due to performance issues and errors. Use this metric to evaluate how well your app handles repeated activity over time. To improve the results, you can adjust the test scripts or system resources.
Application response
Application response is a particularly important metric for ensuring user experience. It measures how quickly the app completes a user action or request, most often in milliseconds or seconds. In stress testing, you are able to see how response times change under extreme loads. This is crucial for eliminating the risk of slow or inconsistent response times, which can frustrate users and reduce the reliability of your system. If you monitor this metric, you will be able to pinpoint the areas that need optimization: for example, database queries, server processing, or frontend performance. If you keep application response times low, you will ensure that the system remains usable even under heavy stress.
Hittime
When you measure hit time, you can see how much time it takes for a server to respond to a single request: for example, loading an image or script.
During stress testing, it is possible to evaluate whether hit times remain consistent regardless of the number of requests, especially when this number is growing.
If you notice slowing hit times, it’s likely due to issues like slow disk access or the insufficient capacity of the server. If you optimize content delivery and server performance, you will be able to reduce hit times and improve overall user experience.
Time to the first byte
Time to the First Byte, often abbreviated as TTFB, is the time it takes for the server to send the first byte of data after it receives a request from a user. This is one of the most important metrics that help you measure how responsive the server is under stress. In case of high TTFB, it’s possible that your servers are overloaded or that your app’s logic is inefficient. If you lower TTFB, you will ensure that pages load faster even during high traffic.
Page time
Page time is a metric that measures the total time it takes for the system to fully load a web page, including all its resources like images and scripts. In stress testing, you are able to see how heavy traffic affects page load times. You want to avoid slow page times at all costs because they can frustrate users and even lead to higher bounce rates. The most popular reasons for slow page times are unoptimized scripts and large media files. If you deal with these issues, you will be able to improve page load performance and, thus, the user experience of your app.
Failures
Last but not least, failures track the number of errors and crashes that occur in your app during a stress test. The scope includes server errors, app exceptions, and system crashes under heavy load. Usually, a high failure rate shows that the system can’t handle extreme conditions effectively.
Most frequently, the root causes of failures are memory leaks and resource exhaustion. If you reduce failures, you will be able to ensure that the app remains reliable and functional under stress.
Failed connections
This metric helps you count the number of connection attempts that fail during a stress test. Quite often, failed connections are direct results of overloaded servers, insufficient resources, or even network issues. A high number of failed connections is likely to disrupt user access and harm the reliability of your product in the long run. Stress checks help you identify these issues and fix them on time so that your application remains accessible and smooth even during traffic spikes.
Failed rounds
Failed rounds measure how many test rounds weren’t completed successfully. Usually, these failures result from errors in the application itself, server crashes, and network issues under stress. During a stress check, you will be able to define the conditions under which it happens and eradicate them. When you reduce failed rounds, you enhance the reliability and performance of your app.
Failed hits
At last, failed hits count the number of individual requests that result in a failure from the server’s side. For instance, missing files or server-side exceptions. In stress testing, you can see how often failed hits occur under heavy loads and extreme traffic. When you address problems like poor error handling, the exhaustion of resources, and the misconfigurations in the server itself, you will be able to improve the stability of your app with fewer errors.
How to perform stress testing?
In web apps testing services it is important to build a proper strategy first. Stress testing can be an ambiguous and non-linear process when different issues occur at the same time, and it becomes gradually more difficult to keep track of the problems and system conflicts you need to address during maintenance. Before you begin to troubleshoot your product, make sure to draw up an algorithm on paper and follow it to make the process easier and more streamlined.
The crucial steps for stress testing process:
Identifying test scenarios
Start by learning how users interact with the app. Focus on areas that are likely to experience heavy traffic - login pages, checkout processes, or data uploads. Look for actions that require significant server resources. Identify scenarios where multiple users might act at the same time. Include edge cases, like rare or unusual user behaviors. Prioritize scenarios that are critical for app performance and user experience.
Defining test goals
For the next step, clearly state what you want to achieve with the test. Goals may include finding the system’s breaking point or ensuring stable performance under heavy load. Define specific metrics like response time, throughput, or failure rates.
Decide the limits for acceptable performance, such as maximum load before crashing. Focus on measuring resilience and recovery under extreme conditions.
These goals guide the design and execution of the test and ensure meaningful and actionable results.
Designing test cases
Create test cases that mimic real user actions. Include tasks like browsing, searching, or completing transactions. Set parameters like the number of users, request frequency, and data size. Plan test cases for both expected and extreme usage conditions. Ensure the test cases cover all identified scenarios. Use automation tools to execute test cases efficiently. Design tests to provide clear data for analysis and improvements.
Preparing the test environment
Before stress testing software, it is important to create an adequate environment that includes all the provisioned tools for simplifying the testing process.
Setting up a test environment for production simulation
Set up an environment that mirrors the production setup. Include the same hardware, software, and network configurations. Ensure the system has the necessary monitoring tools installed. Verify that all dependencies, like databases or APIs, are functional. Double-check that the test scripts are correctly configured. Isolate the environment to avoid impacting live systems. Test the setup briefly to confirm everything works before starting.
Execution of stress tests
Start the test with the defined scenarios and parameters. You can use a fitting stress test tool like Apache JMeter, LoadRunner, or Locust. Gradually increase the load to observe the system’s behavior. Monitor key metrics like response time, throughput, and error rates. Keep track of any failures, crashes, or slowdowns.
Analyzing test results
Review the data collected during the test. Focus on metrics like response times, throughput, and failure rates. Identify bottlenecks, such as slow database queries or server overloads. Look for patterns, like performance drops under specific conditions. Compare results against your test goals and benchmarks. Prioritize the issues that most affect user experience. Use insights to create a clear action plan for improvements.
Reporting and action
Finally, summarize the results in a simple, clear report. Highlight the system’s strengths and weaknesses. Include key metrics, bottlenecks, and failure points. Recommend specific actions to fix issues and improve performance.
Share the report with all stakeholders, like developers and managers. Plan and execute the necessary improvements based on findings. Retest after changes to ensure the system meets the desired performance.
Common stress test mistakes
Even the most experienced and highly skilled web stress tester can’t fully avoid some of the most common mistakes in stress testing. However, with a sufficient level of preparation, it’s possible to prevent minor problems before they grow into issues that will be hard to fix. Here’s what you should be wary of and avoid at all costs.
Incorrect configuration
The most critical mistake you can make during stress testing is setting up the test environment incorrectly. For example, if you use hardware or network setups that are different from the ones planned out in the production. This difference is likely to give misleading results to your checks. If your test environment doesn’t match the real-world setup in which the app will be installed and used, the results won’t show how the application will behave under an actual stressful situation.
Besides, you can accidentally choose the wrong configurations for test parameters: unrealistic user behavior or traffic patterns that are unlikely to occur in real life. As a result, you will either underestimate or overestimate your product’s performance.
To avoid this, always use the test environment that is as close as possible to the production setup. Also, test scenarios should be carefully designed to reflect real-world conditions that can actually occur. Review your configurations with stakeholders regularly so you can identify potential issues early on.
Monitoring gaps
During stress testing, it’s important to monitor all the relevant performance metrics as the test unfolds. It won’t be enough to just track response times: in addition to that, make sure to monitor server CPU usage, memory consumption, network bandwidth, and the performance of your database.
If you fail to track any of these metrics, your analysis will be incomplete, which will make it hard to identify issues. For instance, if you forget to check the memory usage of your app, you might easily miss a memory leak, which can lead to serious repercussions later or even immediate negative consequences.
Make sure to use comprehensive and adequate monitoring tools and draw up a clear list of metrics to measure before you launch the test itself. Enable logs and error reports in advance so you can analyze all the present issues and failures in detail.
Mismanagement of different types of testing
If you focus only on stress testing and don’t consider necessary endurance tests, you will likely overlook important long-term issues, such as memory leaks. Each type of test has its purpose and is crucial in its own right, and if you mix them up or fail to consider at least one, your workflow will be inefficient, and you will likely miss a lot of potential issues.
Before you start testing, clearly define the objectives of each type of test and ensure that your team members understand the differences between them, as well as the purpose of each test. Once you achieve this clarity, it will be easier to ensure that tests are both meaningful and effective.
Conclusion
What are the 3 types of stress tests that you need for a successful app launch? Ideally, stress testing, and endurance testing are a must before your application goes global. However, a larger scope of checks and troubleshooting might be required depending on the nature of your app and the features plan to implement. Reach out to the DeviQA experts to enhance your testing processes.
Team up with an award-winning software QA and testing company
Trusted by 300+ clients worldwide
