Recall your last shopping trip — you may have spent half an hour wandering from aisle to aisle, choosing goods. But when it came time to pay, the process took just a second. That seamless experience is thanks to a well-integrated, flawlessly functioning POS system. Most people take it for granted — until something goes wrong.
Stats show that 81% of retailers experience POS downtime at least once a year. For example, back in 2022, many merchants across Germany experienced a major disruption when Verifone H5000 payment terminals went down. For several days, card payments couldn’t be processed due to a technical malfunction — a real nightmare in a country where 60% of retail transactions are made by card.
To avoid such chaotic scenarios that cost businesses a fortune, POS software testing should be done comprehensively and continuously. Loaded with years of experience, DeviQA reveals the most efficient testing strategies and best practices to help you avoid costly POS failures.
POS testing: not an option but a necessity
These days, point-of-sale software lies at the core of the retail and service businesses. While performing its core function – processing payments – it also handles in real time a great number of other critical operations, such as inventory management, customer relationship management, fiscal documentation generation, reporting, data analytics, etc.
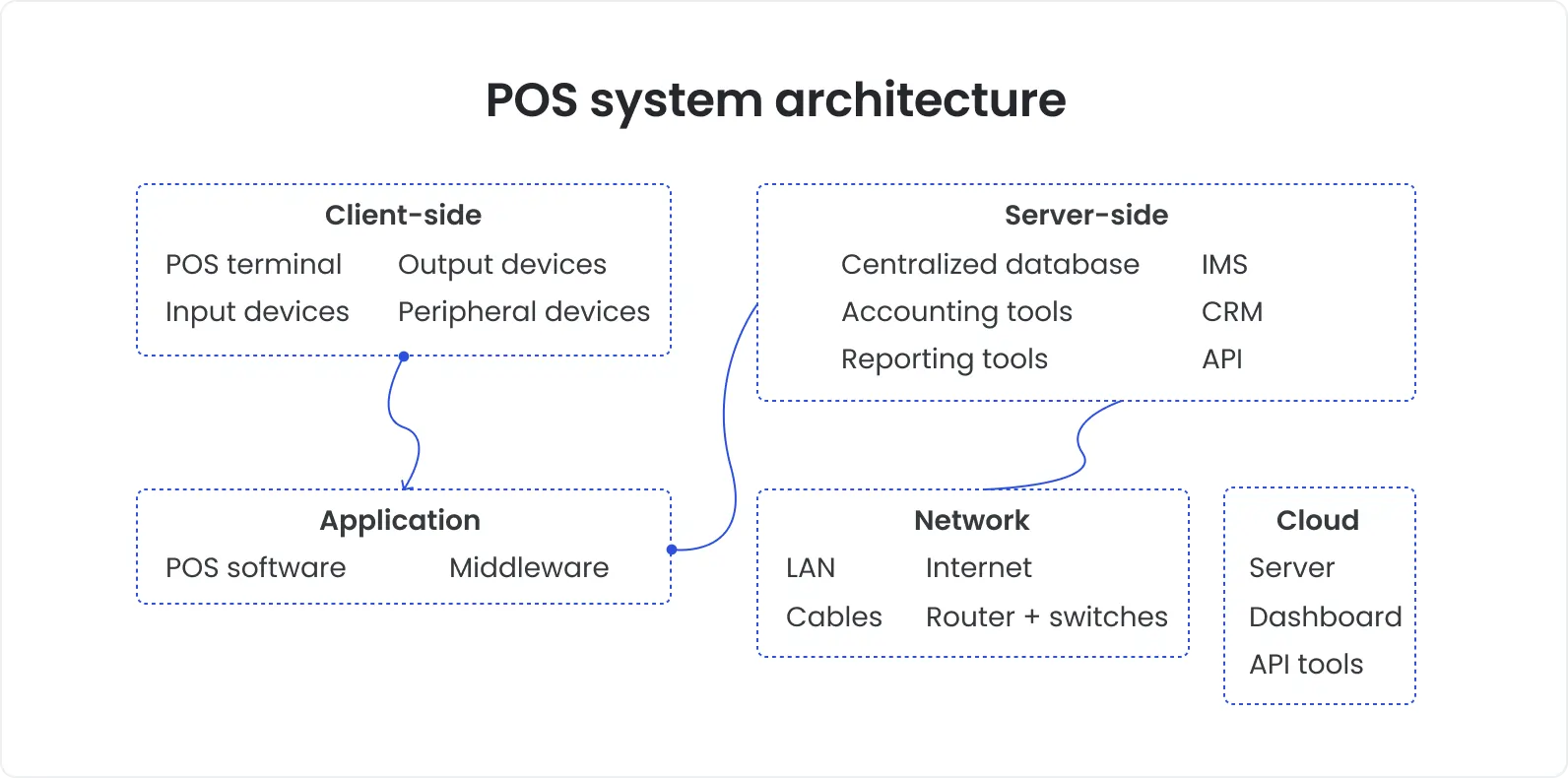
Whether traditional POS systems, mobile POS systems, or self-checkout kiosks are used, a fast, seamless experience is expected, and anything less can immediately affect customer trust.
Point of sale software testing is, therefore, essential. Thorough testing guarantees that point-of-sale software functions flawlessly on a variety of devices and under a range of loads. Revenue, consumer trust, and operational efficiency are all impacted by this.
Inadequate testing of POS systems can lead to severe consequences. Usually, troubles come at the most inconvenient time and from where you didn’t expect. The Verifone H5000 case mentioned in the very beginning isn’t the only one.
In 2017, Macy’s, an American department store chain, faced nationwide problems with its POS system on the busiest day of the year – Black Friday. It ended up with long queues, unhappy customers, plentiful complaints on social media, lost revenue, and significant reputational damage.
Two years later, Marc’O Polo fell victim to a ransomware attack that encrypted all its IT systems, including POS terminals. The company faced operational shutdowns and delays in customer deliveries, resulting in millions in losses. And that’s no exaggeration – according to the ITIC report, the average cost of just one hour of downtime for a business is $100,000.
Payment glitches during peak hours, failed checkout transactions, and full POS outages always lead to painful consequences: lost sales, damaged brand reputation, and expensive recovery efforts.
Therefore, working with a seasoned QA partner for POS testing is a strategic move. Outsourcing to a specialized software testing company streamlines QA processes, safeguards uptime, and reduces potential risks.
Key challenges encountered during POS application testing
As software of any other type, POS apps have certain peculiarities that impose challenges in the course of testing. However, seasoned QA engineers know them and the ways to address them efficiently. Let’s take a look at these challenges:
Hardware diversity
POS software interacts with a lot of physical devices — barcode scanners, receipt printers, payment terminals, cash drawers, and card readers. Ensuring smooth communication between the software and the hardware is rather challenging. Each of these devices has its own firmware and connectivity requirements. Even a tiny inconsistency, like a delayed signal from the printer, can disrupt the entire checkout process. Cross-device testing ensures these devices initialize correctly, reconnect without hiccups, and function as intended in a variety of scenarios. Without careful validation, businesses may experience transaction delays, misreads, or complete functionality breakdowns.
What to test in hardware integrations:
Device initialization and shutdown behavior
Reconnection after temporary disconnects
Compatibility across different manufacturers
Response timing during peak hours
Multi-device usage during a single transaction
Support for multiple payment methods
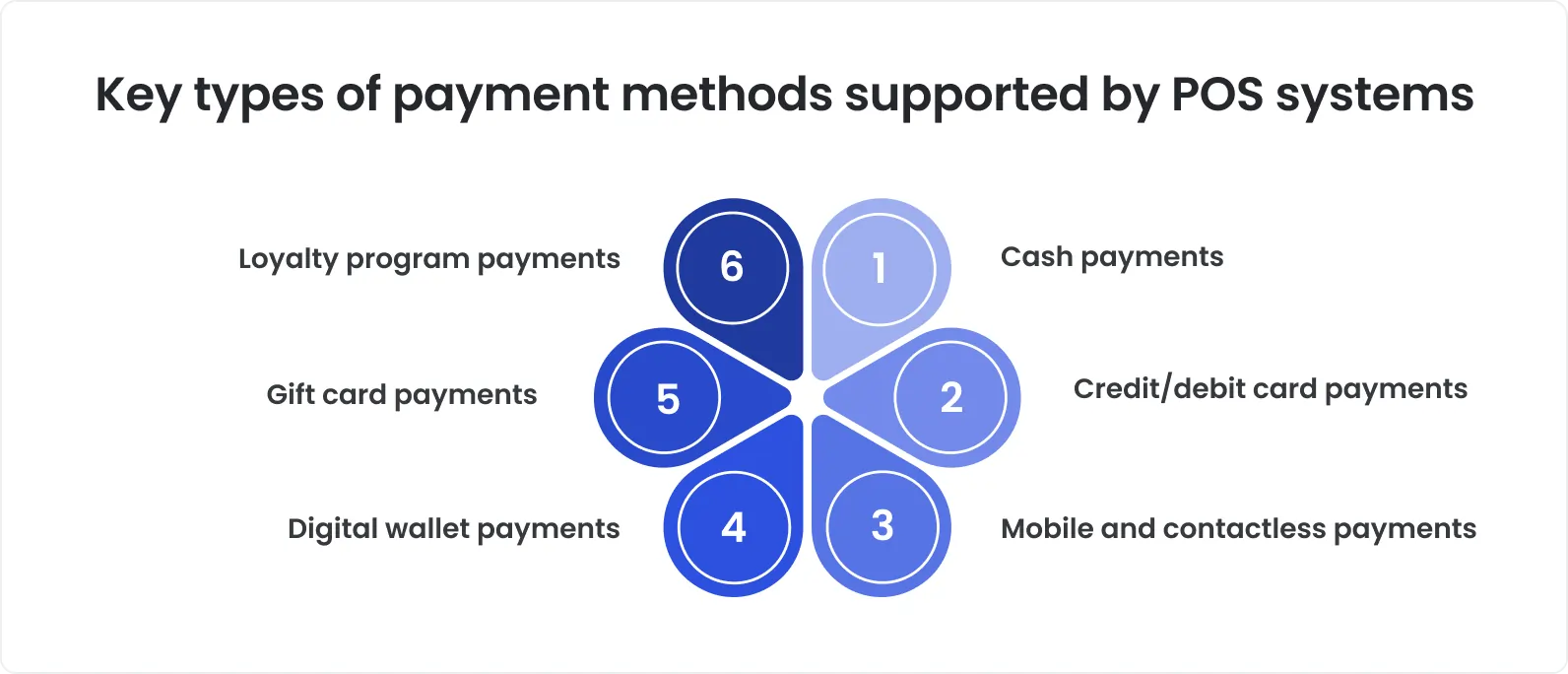
Modern POS systems support numerous payment methods, each of which needs to be validated across different transaction types, currencies, and tax settings. All possible scenarios, including successful transactions, declined cards, partial approvals, timeouts, refunds, and network interruptions, must be carefully tested.
Key checks for payment method validation:
Transaction processing for each payment type
Handling of multiple currencies and taxes
Support for partial approvals, split payments, and refunds
Offline mode and poor network conditions
Security validation, including tokenization and PCI DSS compliance
Real-world condition simulation
In reality, POS apps operate in diverse, often unpredictable settings with varied volumes of concurrent transactions, network types, hardware configurations, user interactions, etc. It can be difficult and resource-intensive to replicate such conditions in a test lab, but without these simulations, it’s hardly possible to uncover hidden performance bottlenecks, data sync issues, or usability flaws that may arise in a real-world environment.
Real-world simulation scenarios worth covering:
Peak-hour transaction volumes
Unstable Wi-Fi/mobile network environments
Unexpected shutdowns and power loss recovery
Simulated delays in external service responses
Parallel transactions across multiple terminals
Integration with external services
To be multifunctional, modern POS systems integrate with different payment gateways, inventory management systems, ERP tools, loyalty platforms, and CRM platforms. Each of these integrations creates a point of potential failure if not tested thoroughly. Verifying accurate data transfer between a POS app and integrated systems is a complex task that shouldn’t be overlooked with additional ERP software testing or QA for CRM.
Aspects requiring particular attention:
Real-time sync and latency validation
Fallback behavior when integrations fail
Data consistency after retries or reconnections
Long test cycles
Taking into account the complexity of POS apps and associated security and financial risks, their testing covers a lot of aspects, including functionality, compatibility, performance, security, integration, data backup, usability, and many more. This may result in long test cycles that delay deployment, impacting business operations. However, software testing companies provide managed testing services with advanced testing tools, efficient techniques, and best practices like agile software testing to streamline QA processes while maintaining high test coverage.
Best ways to manage long test cycles efficiently:
Automated regression and smoke testing
Test prioritization based on risk and business impact
Implementation of CI/CD pipelines for continuous testing
Breaking down testing into agile-friendly increments
5 best QA practices to optimize testing and save you from costly POS failures
As an experienced provider of retail software testing services, the DeviQA team is happy to share best practices that improve POS testing efficiency and save time and costs.
1. Execution of end-to-end testing
Testing of isolated app components cannot bring the desired results. End-to-end testing needs to be executed to validate the entire user flow, from product scanning to receipt printing and transaction syncing in the cloud.
A full e2e test might comprise scanning a few items, applying a discount, using a gift card, making an NFC payment, receiving a digital receipt, and adding the sale correctly to the backend dashboard.
We advise using real devices for testing, where applicable, and replicating real-time scenarios like device disconnections or cashier errors during the workflow.
2. Prioritization of performance testing
POS systems must perform flawlessly and stably not just under normal traffic but also during peak loads or long operating hours. Yet, performance bottlenecks often don’t reveal themselves until the POS system is put under stress.
Black Friday, holiday sales, or new product launches can cause traffic surges that may break fragile systems. Therefore, POS applications must undergo comprehensive performance QA testing to exclude the possibility of downtime, memory leaks, crashes after prolonged use, and delayed responses.
Key performance tests
• Transaction processing speed under load
• Queue handling
• Resource utilization (CPU, memory, database I/O)
• POS system behavior under extreme volume
• Error messaging and recovery behavior
• System reboot or restart handling
• Latency during and after a spike
• Impact on connected hardware
• Impact on backend integrations
• Long-term stability of the system and hardware
• Caching efficiency
• Response time trend over hours and/or days
• Performance on different hardware setups
• Adding more terminals/users without degradation
• Horizontal/vertical scaling capabilities
To simulate normal and extreme loads, use tools like JMeter or Gatling. Also, track CPU, memory, and database response times during lengthy test runs.
3. Testing an app for compatibility with hardware
As was already noted, POS software interacts with different devices. Even a minor issue like the failure of a printer to reconnect after unplugging can cause serious troubles.
To detect possible issues early, create a comprehensive compatibility matrix that lists all supported hardware models, manufacturers, connection types, and their corresponding firmware versions. This matrix will serve as a testing blueprint, ensuring coverage across real-world configurations.
Also, don't forget to check firmware updates, as they can silently introduce incompatibilities. Make it a common practice to validate your POS software against new firmware versions early in the release cycle.
4. Test automation
With regard to an extensive testing scope and frequent POS app updates, it makes sense to automate testing to mitigate the risk of human error, ensure app stability across releases, and shorten test cycles.
Tests that are worth automating for POS systems are the following:
Repetitive and time-incentive tests like regression and smoke tests
Data-driven tests
Cross-browser and cross-device tests
Security tests
UI consistency tests
There are a plethora of test automation tools available now. When it comes to functional ones, you can choose between Playwright, Selenium, and others.
Whatever tool you opt for, keep test scripts modular and data-driven to ensure easier test suite maintenance as the POS app evolves.
5. Emphasis on security and compliance testing
POS apps deal with various sensitive data. That's why they must abide by different security regulations, including PCI-DSS standards. Only one non-compliance or vulnerability can lead to data breaches, legal issues, heavy penalties, and damaged reputation.
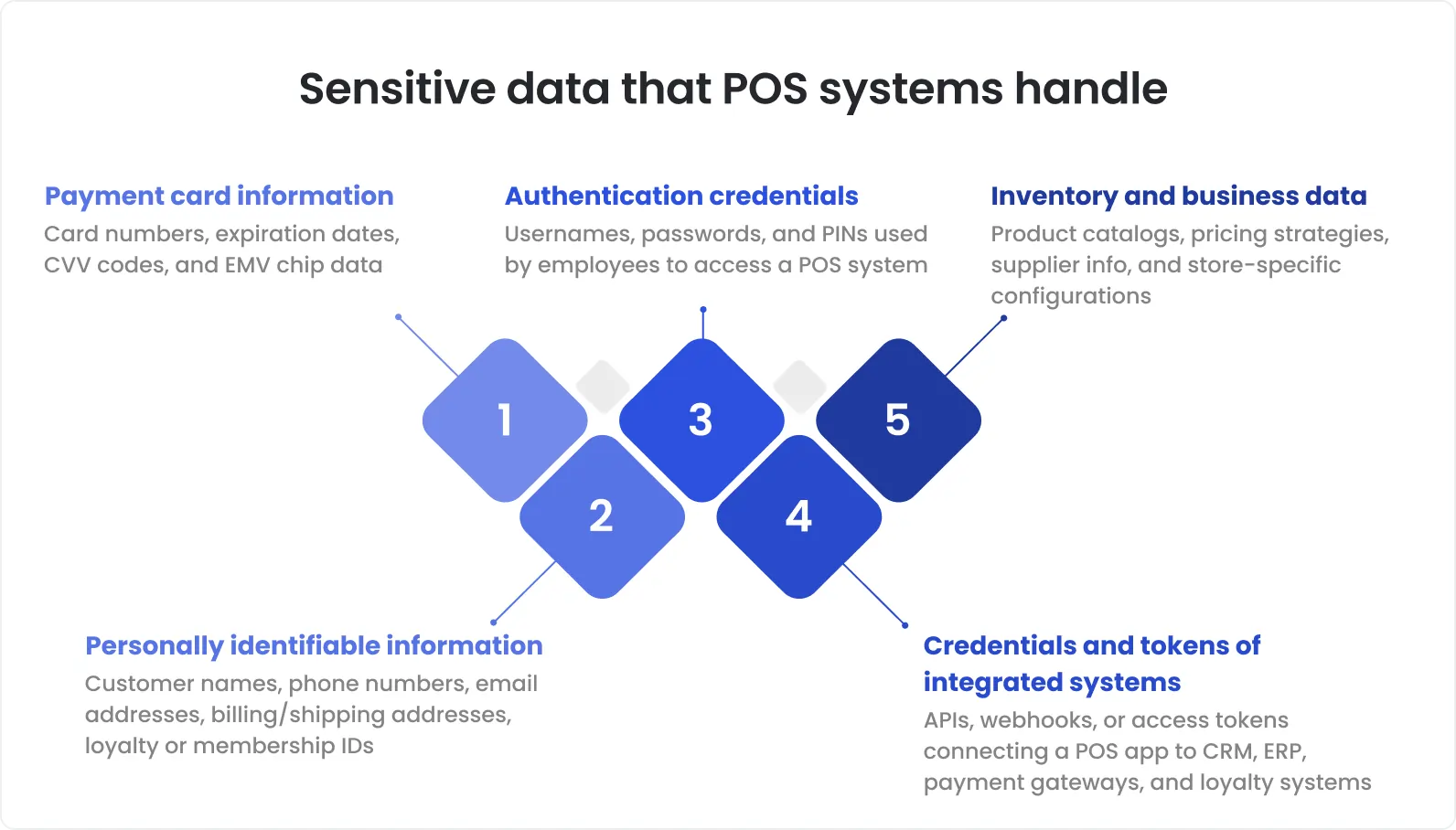
To avoid troubles, POS apps must undergo comprehensive compliance audits, vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, encryption validation, and access control checks. It’s essential to make sure that data in transit and at rest is properly encrypted and that only authorized users can access administrative features.
Bring in QA specialists with deep experience in testing strictly regulated systems and automated security testing.
Tools to automate POS app testing
Effective POS app testing often relies on automation that helps carefully verify different QA aspects. It handles everything from regression checks to complex load simulations and vulnerability scans. Below is a table representing leading test automation tools.
Selenium – for automating browser-based POS systems
TestComplete – for UI test automation of desktop, web, and mobile apps
Playwright / Cypress – for fast automation of web-based interfaces
Appium – for mobile POS solutions on iOS and Android
Ranorex offers support for hybrid tech stacks and peripheral simulation
Tip: Choose tools that support your POS environment and allow data-driven and modular scripting for easier maintenance.
JMeter – a highly customizable tool for web services and protocols
Gatling – a lightweight tool suitable for scalable load testing
LoadRunner – an enterprise-grade solution for simulating complex user behavior
Locust – a Python-based and developer-friendly tool for simulating concurrent users
Tip: Use tools that can reproduce realistic loads and help visualize response times, throughput, and failure points.
OWASP ZAP – an open-source tool for detecting security vulnerabilities
Burp Suite – for advanced web security testing
Veracode / Fortify / SonarQube – for static and dynamic code analysis
Nessus – a tool for vulnerability scanning used also for connected devices and services
Qualys – an enterprise-level compliance and vulnerability scanning tool
Tip: Regularly run security tests as part of CI/CD and use the delivered results to strengthen the POS app and the infrastructure.
Postman – for manual and automated API tests
SoapUI – for functional, load, and security testing of both REST and SOAP APIs
REST Assured – for automating REST API tests as part of integration test suites
Tip: Mock external services to isolate POS apps during test runs and include negative tests for failed transactions, bad data, and timeout handling.
Correctly chosen and properly used test automation tools streamline a QA process, save time and cost, and improve test accuracy. When selecting tools for testing your POS application, pay attention to the following criteria:
Scalability
As your POS app evolves and becomes more complex, your testing needs will grow. A decent tool should efficiently handle increasing test cases and test data volumes, support parallel test execution, and adapt to new app features without necessitating extensive revamps.
Tech compatibility
Compatibility of a tool with the technologies used in your POS application is an important selection criterion. For instance, for testing native mobile POS apps, Appium or Espresso might be appropriate. For web-based POS dashboards, Playwright or Selenium could be a good fit. Also, make sure the tool works well with the needed operating systems, devices, and communication protocols. Incompatibility can lead to unreliable tests or excessive customization efforts.
Integration readiness
Test automation tools usually don’t operate in a silo. Choose tools that will plug into your CI/CD pipelines (e.g., Jenkins, GitLab, GitHub Actions), test management platforms (e.g., TestRail, Zephyr), and cloud infrastructure (e.g., AWS, Azure) to support distributed and scalable test environments. Tools with rich APIs or plugins make integrations smoother and reduce manual steps in your workflow.
Reporting and analytics
Testing is valuable when insights are clear. Therefore, your test automation tools should offer detailed logs, screenshots, customizable dashboards, and alerting mechanisms for failed tests in CI/CD pipelines. Opt for tools that provide both high-level summaries for business people and deep technical data for QA engineers.
Learning curve
Even the most brilliant tool is ineffective if a team can't use it efficiently. Check if your team has the required skills and if community support, guidelines, and training materials are available. If there are any doubts, you’d better start with a pilot project in order to test usability and fit before full adoption.
Don’t want to bother yourself with all those hassles? A trustworthy outsourcing software testing company can handle all QA-related tasks, including automation tool selection. With rich expertise in choosing, configuring, and integrating tools, they quickly build robust test automation solutions that ensure comprehensive, scalable, and efficient testing.
Advantages of effective POS app testing
Testing is a must for POS systems of all types. This is the only way to ensure flawless POS work under various conditions. Functional, performance, security, usability, compatibility, integration, backup, recovery, and other tests help ensure that your system is reliable, safe, efficient, and ready for real-world demands.
• Accurate calculation of prices, taxes, and discounts
• Solid protection against cyberattacks
• System stability in peak business hours
• Regulatory compliance
• Operational efficiency
• Seamless integration with third-party systems
• System interconnectivity
• Streamlined customer experience
• Consistent data management
• Transaction failures
• Downtime during peak hours
• Data loss or corruption
• Inventory discrepancies
• Security vulnerabilities
• Heavy penalties due to regulatory non-compliance
• Inaccurate reporting
• Poor user experience
• Loss of customer trust
• Damaged brand reputation
• Lost revenue
As a result, you minimize operational disruptions, protect your brand reputation, and retain customer trust. Ultimately, efficient point of sale testing safeguards and even boosts your revenue.
To unlock these advantages, you need to bring in highly professional QA engineers who can carry out holistic testing. Look for teams with both deep technical knowledge and industry-specific experience, because excellence in POS testing requires both.
Conclusion
Nowadays, POS systems are widely used in retail, hospitality, and other industries. According to the Salesforce 2020 Small & Medium Business Trends Report, for 50% of small businesses, analytics and reporting provided by their POS systems play a key role in running their operations.
POS failures are simply not an option. Thorough testing, while associated with certain challenges and requiring time and resources, is essential for ensuring the seamless work of POS apps.
Experts in POS software testing embrace automation, prioritize e2e and performance testing, validate security and regulatory compliance, and check the app for compatibility with diverse hardware. These practices let them ensure the high quality of POS apps and protect businesses from costly failures.
There is no doubt that the demand for software testing services will grow as POS technologies continue to advance. Far-sighted businesses that intend to fly high invest in forward-thinking, adaptable testing strategies.
What about your QA approach? Are you happy with it? If there’s room for improvement, the team at DeviQA is here to help you take it to the next level.
