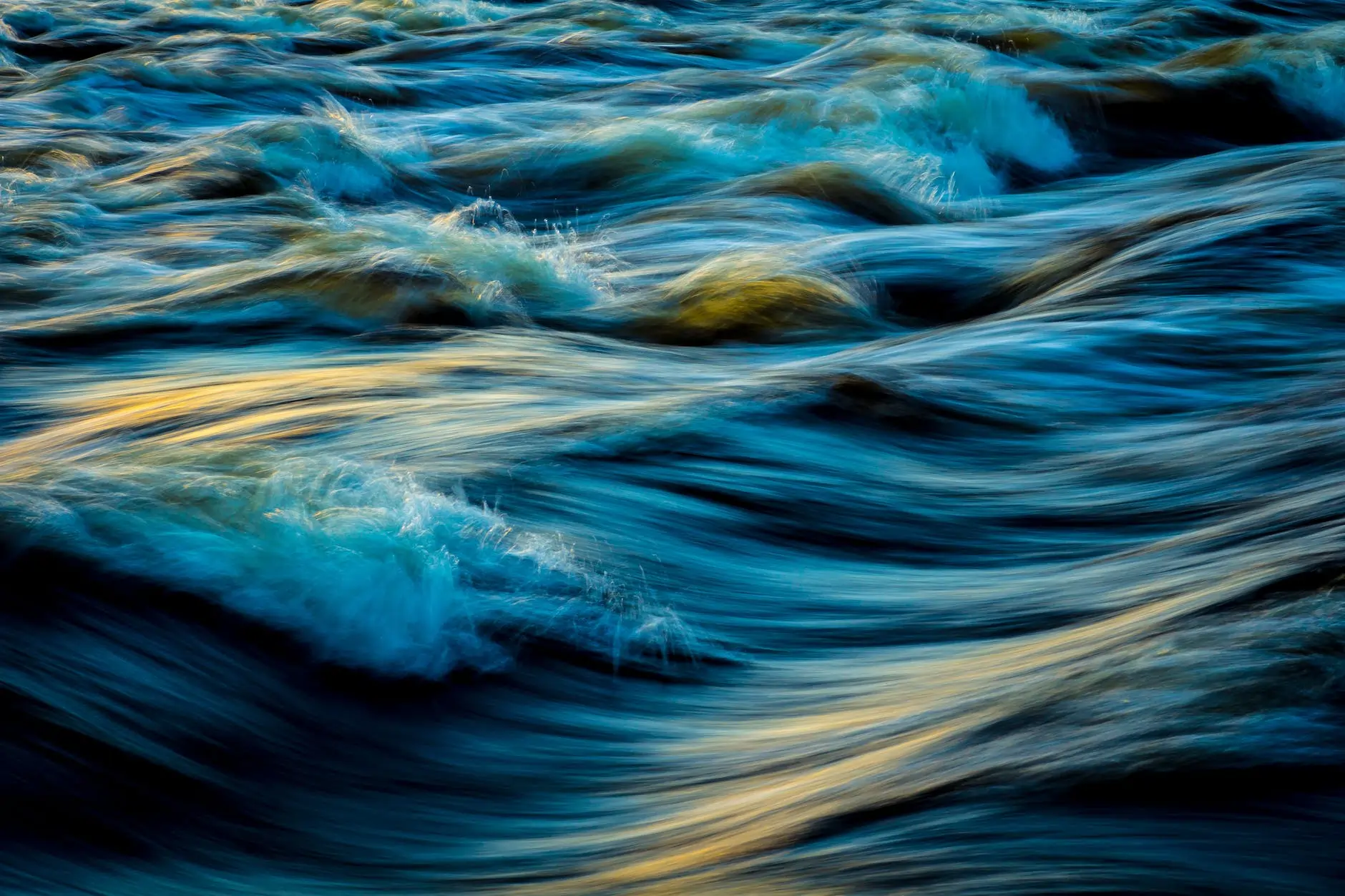
Merely functional and simple load testing is no longer enough for testing sites today. They do not provide confidence in the performance of applications in the real world and now require more sophisticated means.
With the advent of Web 2.0, sites have become interactive. They have learned to recognize their visitors and adapt to their expectations. Users, in turn, have become more demanding for sites, expecting them to understand requests at a glance and provide an adequate result instantly.
All this has led to a tremendous increase in the load on the web servers and tighter requirements on the level of service. Any delay or error in the site leads to the loss of visitors. The efficiency of the site has become critical for most businesses today, and the price calculation in the assessment of its actual performance has increased significantly. All this makes load testing up-to-the-minute.
What is Web Based Application Testing?
Today we use two approaches to automate the creation of load testing and testing load. The first is the creation of multiple copies of the browser performing user's' actions in the automatic mode. In this case, we reconstitute an interaction session with a real user, which, however, requires a large number of resources.
You can run no more than a hundred copies of concurrent browsers on one computer of conventional architecture. Therefore, for the modeling essential load, it's necessary to deploy a network of computers. The second approach is HTTP-requests emulation where user's actions are emulated, but you can create thousands of virtual users on the same computer.
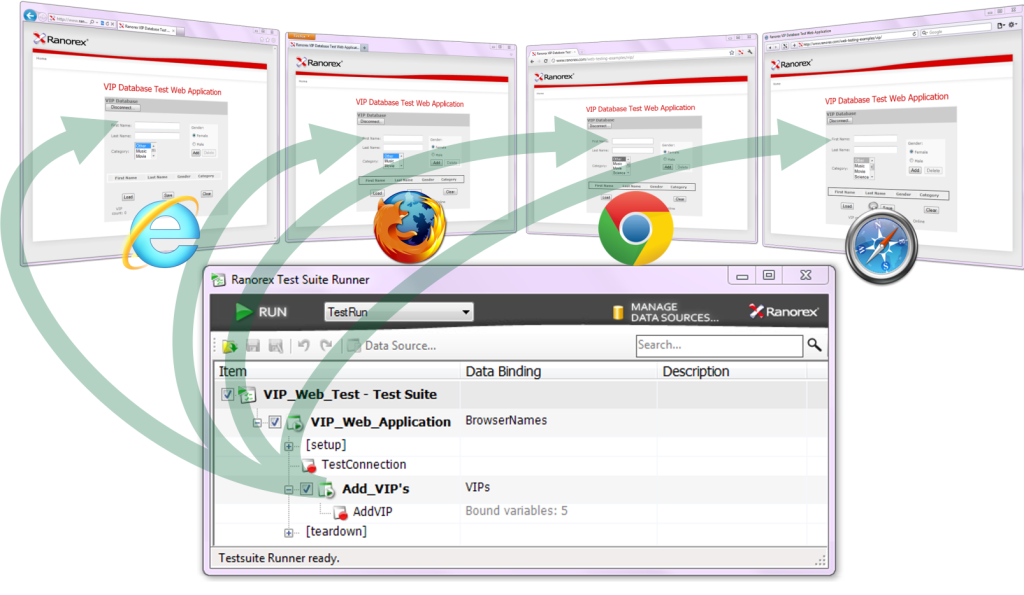
What Products to Use for Testing Web Applications?
Products for performance testing can be divided into three classes: free; corporate, having all imaginable functionality; cheap generic.
The first category includes a product like Jmeter, which may require a high cost of ownership including the involvement of expensive specialists. Also, the product is not supported, and creating a test process can take too much time.

The second group includes products such as HP LoadRunner, IBM Rational Performance Tester, and Borland Silk Performer, allowing to automate the process of load testing, speed up and significantly improve its quality. For example, LoadRunner functionality can satisfy even the most demanding testers. The product has almost everything for different kinds of test, but its cost is high, and development requires time to study all the features and possibilities.
The third group includes such products as PureLoad, NeoLoad, and WAPT, which are easy to install and configure to perform load testing of web applications that are running on any OS.
What are the features of web application performance testing?
Here is the main function of testing in modern web environments, what testers have to face and what requirements should the tools satisfy to automate the testing process:
Dynamic sessions
A current website is a multilevel application consisting of firewall, load balancer, multiple web servers and application servers, and databases. To "assess" their visitors, most sites have to maintain individual user sessions and work with constantly changing data. This flexibility results in the need for tests to verify operability of such sites also be changed "on the fly."
This has led to the emergence of a new data-driven testing methodology, which imposes certain requirements for solutions for web application testing. The test should be data-driven, which means that each virtual user should have its set of experimental data. This user should look unique for the site, different from other "visitors" able to work with server responses.
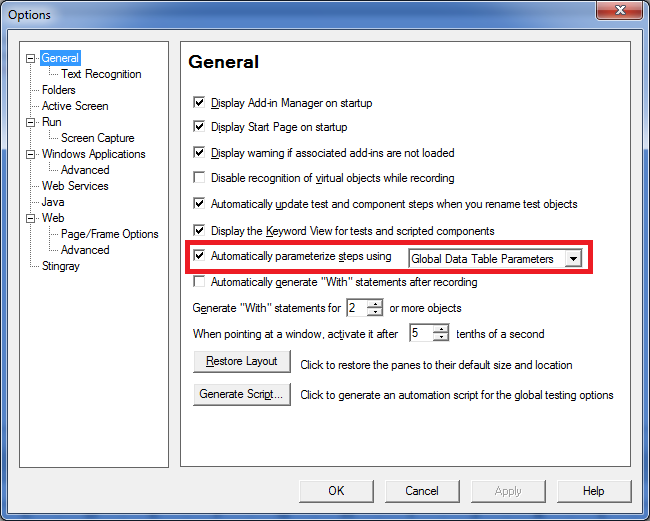
Auto-parameterization
When creating cool websites, agile development is becoming increasingly common. The development process is divided into a series of quick iterations, each of which passes a full-cycle from the formation of the requirements to getting a working version that implements these requirements.
As changes to the system are frequently made, so tests for the created web applications have to change more often. This requires a means of stress testing to quickly create a new test scenario.
Response validation
Modern sites in case of error do not show the error code and message of the emergency situation to users, so a key responsibility of the server has to be checked for the correctness of the implementation. The load testing tool should allow the tester to specify criteria for server responses.
Testing an inadequate system
Typically, software testing is conducted in an environment that is different from the working one (resources, means of load balancing, and so on). So the common problem is the disparity between test and production systems. Often, due to the lack of resources or testing programs limit tests carried out on cheap equipment and simulate fewer users than expected on a working system.
As a result, it may form an inadequate assessment of the performance of the test system, and some of the problems can be not revealed. Often, testing does not take into account the geographical distribution of the load, which normally has a wide scatter of user connection speed and response time. However, on the working system, it may lead to specific problems such as slow users may require more server resources.
Testing on the Cloud
Modern heavy sites are distributed systems, which are often located on the clouds. To test these sites, you will need comparable power resources, so load testing is also advisable to carry out on the clouds. Being on the cloud, it is possible to test both from outside the perimeter of the protected site, and from the inside. This, in particular, to determine the effect of the firewall and a load balancer system performance.
Performance Monitoring
Web application testing is not just determining the system performance, but also finding its bottlenecks. Collecting data on the system under test (CPU usage, memory usage, and disk subsystem utilization of network interfaces, performance data of web servers and database servers) lets you find its bottlenecks that lead to performance problems.
What is Web Application Testing: Tools and Methodology?
On the market today, there are some universal, simple load testing tools that enable the majority of developers and testers to build robust websites. As an example is the series of WAPT product options which are typical for this class of solutions.
These systems allow you to organize local testing at small loads of up to 2 thousand virtual users and a distributed one with the simulation of high loads. Also, the series of agents are available for testing on the cloud and from the cloud. The products can be used to test any web application that runs under the HTTP(S) protocol, except some certain proprietary protocols (for example, RTMP).
To create a virtual user profile, you should perform all of the actions in the selected browser while a special browser recorder will record a sequence of queries and parameterize the dynamic data. To support dynamic sessions, it's possible to parameterize data in the request: the request header, cookie data, query parameters in the query string and in the body that lets you to create unique requests.
The parameterization is performed by using a set of functions that allow you to do it without writing code, but JavaScript can be used in particularly complex cases. The operator of cycle, branching, randomization is used to respond to the server and the change of user behavior allowing users to create a different response.
Validation of responses is made by the reply time and its contents. Validation time is applicable in cases where the response time is hard-coded. Validation of the contents allows determining the correctness or fallacy of execution according to the keyword. It is also always possible to manually check the response from JavaScript.
Web Application Testing Tips
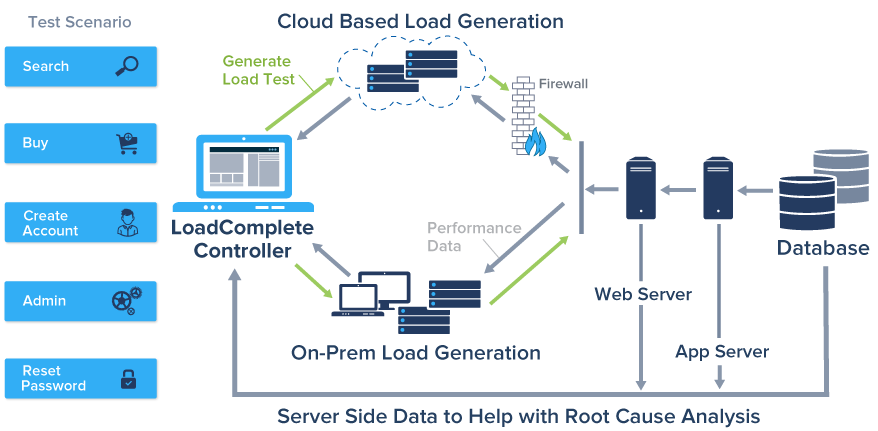
To create a distributed load, there is a "workplace" to run the tests and the agents that create the load. Agents can be located anywhere as for their work you will need access to the test site and the link to the user's "workplace." This lets you to scale and distribute the load simulating the work of the required number of users. You can also change the speed of an individual virtual user that lets you to simulate, for example, the behavior of slow-moving users accessing the application through 3G networks.
The products of this type should also have a means for deployment on the public cloud such as Amazon. Amazon data centers are located around the world; it will let choose the most convenient place for testing geographically distributed load.
To improve the quality of the testing system, the monitoring of the performance of Web servers should be organized, for example, via WMI and SNMP protocols. During the test, you can monitor CPU usage, evaluate the use of memory, disk and network subsystems any server with the help of built-in performance counters, and you can get database specific performance counters via ODBC.


