Oracle services are gaining traction, with the global market expected to rise to USD 63.01 billion by 2033, experiencing a CAGR of 14.82%. Oracle services refer to the various solutions and products provided by Oracle Corporation. Apart from the database, its flagship, and a comprehensive suite of cloud apps, Oracle also offers the E-Business Suite.
While being able to transform businesses, Oracle’s solutions require comprehensive testing due to heavy customization, complex configuration, and frequent updates. Still, profound knowledge of Oracle and specialized skills are indispensable prerequisites for proper testing.
What are Oracle applications, and why do they need specialized testing?
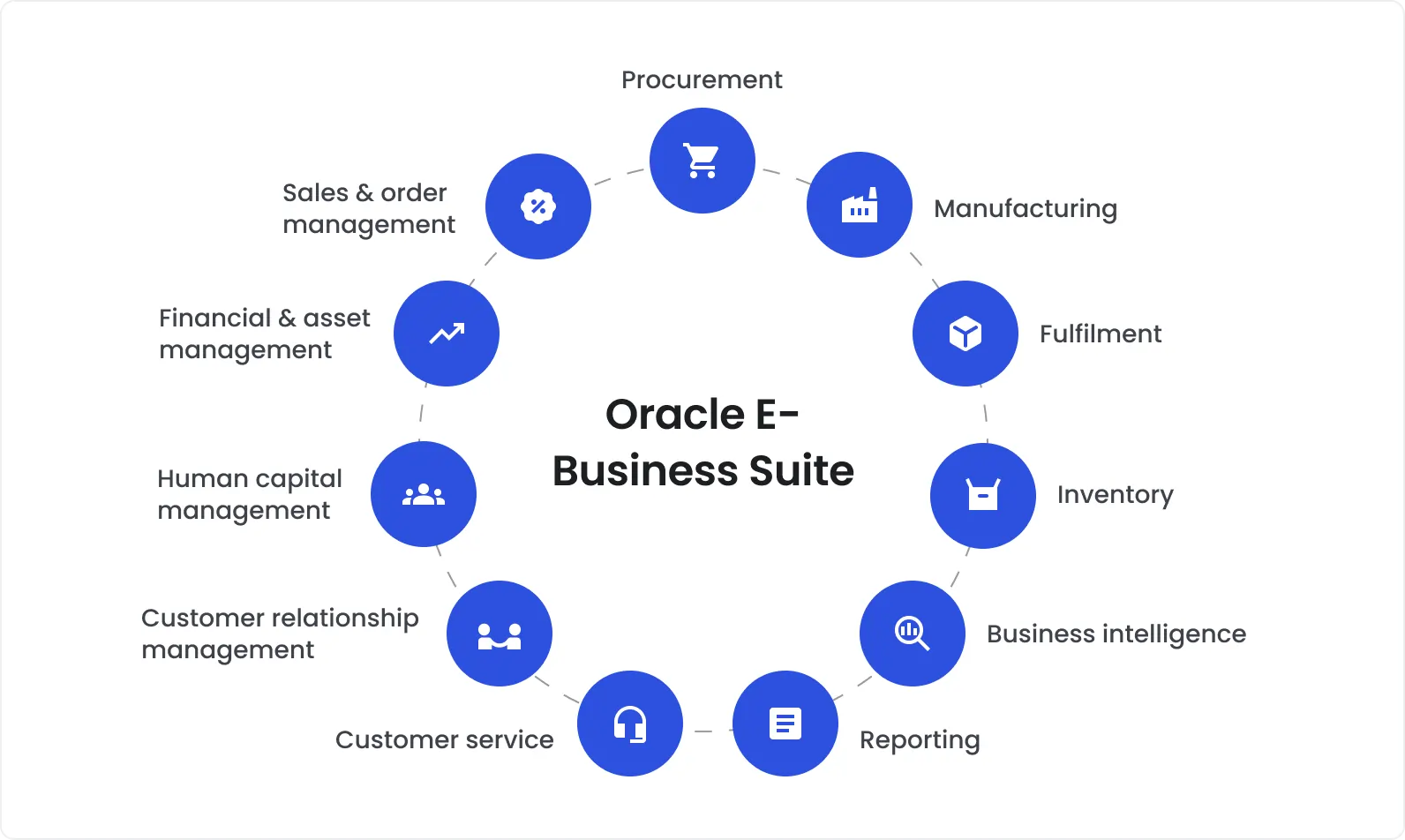
Oracle applications can be defined as enterprise software solutions built by Oracle Corporation to optimize key business functions. Oracle Financials, Oracle Human Resources (HRMS), Oracle Supply Chain Management (SCM), Oracle Manufacturing, Oracle Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Oracle Projects, Oracle Procurement, Oracle Logistics, Oracle Asset Lifecycle Management, and Oracle Order Management are key modules of Oracle E-Business Suite. They are deeply embedded in the operations of large organizations across industries, primarily finance, healthcare, manufacturing, government, and retail.
But with this power also comes complexity and risk. Despite Oracle's robust development and release processes, enterprise use cases introduce unique variables that require tailored testing strategies.
Reasons to test Oracle Cloud applications
Key challenges associated with Oracle app testing
Oracle applications are powerful, but it isn’t as easy to test them. QA teams need to address unique technical and organizational challenges.
Challenge 1: Handling complex interfaces
Different UI technologies, such as Oracle Forms (for legacy systems), ADF, APEX, and the modern Fusion UI, are used within Oracle apps, and far too often, they don’t work well with usual test automation tools. Therefore, QA teams often use manual testing in combination with custom-built test automation solutions. That's particularly relevant when interfaces are significantly customized to meet business-specific workflows.
Challenge 2: Managing data dependencies
There is relational integrity across different EBS modules. Their testing includes not only test data insertion but also cascading relationship management, trigger validation, and referential accuracy checks. Without a robust data management strategy in place, tests become flaky, hard to reproduce, or misleading.
Challenge 3: Checking integrations with legacy and external systems
Many Oracle apps are integrated with older systems, external tools, or in-house middleware. Testing of these integrations suggests validating data transformations, timing consistency, and message protocol compatibility. Among key challenges are unavailable test environments for third-party systems, the need for stubs or mocks, and managing version mismatches during system upgrades. Overlooked defects in integration points often lead to the most costly failures.
Challenge 4: Ensuring high performance in real-world environments
The specific data volumes, workflows, and concurrency levels of your organization can cause performance bottlenecks in an Oracle app, like long-running queries or session contention. Load and stress testing need to be executed to ensure the seamless operation of the app under real-world stress.
Challenge 5: Validating patches and upgrades
Oracle regularly delivers patches, updates, and security fixes. Made changes may affect custom configurations, extensions, or integrations, even if core Oracle code remains stable. Enterprises must execute regression testing in their own environment to ensure nothing breaks. Failure to do so may result in silent failures, corrupted data, or disrupted processes after updates are applied.
Challenge 6: Bridging specialized expertise in
Effective Oracle application testing demands familiarity with Oracle internals, SQL/PLSQL proficiency, and experience with QA testing frameworks. However, it's rather difficult to find his niche skill set – even seasoned automation engineers may face a steep learning curve in Oracle environments. Therefore, app testing in enterprise environments is often not efficient enough.
Why automate testing of Oracle applications?
We have already found out that testing is essential for Oracle apps. Yet, maximum value is brought when testing is automated. Why? Here are some compelling reasons:
Faster testing cycle
Manual regression testing across Oracle’s interconnected modules can take weeks. Automation saves up to 70% of time by executing large test suites in hours, not days. This speed is critical for organizations applying Oracle's frequent updates. It lets a dedicated QA team check all critical workflows and make sure nothing has been affected by a new update.
Better test coverage
Oracle EBS consists of several interconnected functional modules – ERP, HCM, SCM, etc. While testing them, manual testers tend to skip edge cases and backend validations because of a lack of time. Automation, on the other hand, enables more extensive testing that covers backend validations, cross-module workflows, and negative test scenarios, ensuring flawless system operation.
Cost efficiency
Manual testing is time-consuming and effort-intensive, especially when it comes to Oracle’s vast configurations and customizations. Once created, test automation can be reused whenever needed. With regular compliance checks and frequent regression testing executed after each update, automation saves you a fortune over time.
Easier update management
Frequent updates and patches are the norm for Oracle apps, but they may make an impact on configurations, interfaces, or data. Without automation, QA engineers either test manually under pressure or skip some tests. Automated regression tests can run repeatably, quickly, and reliably whenever a new patch or update arrives.
Scalable enterprise testing needs
As Oracle implementations expand with new modules or integrations, test automation scales without increases in labor resources. Teams keep test coverage robust even as environments evolve, ensuring outstanding quality without exponentially growing costs.
Best practices for Oracle test automation
As experts in Oracle-based application testing, we’d also like to shed some light on best practices that ensure test efficacy and help avoid obstacles.
Test prioritization
Obviously, it doesn't make sense to automate all test cases. To gain maximum value, automate those that cover error-prone or critical for business continuity areas of Oracle apps. Our advice is to adopt a risk-based testing approach by defining which business processes would cause the greatest disruption if they failed. The frequency of process execution should be taken into consideration, too. Scenarios that are triggered daily or across multiple departments are most suitable for automation.
Also, check the Oracle update history and define areas of the system that are usually impacted by patches or configuration changes. This will help you align your automation coverage with the most volatile areas, increasing test value over time.
Efficient test data strategy
Test data is key to the reliability of automated tests in Oracle environments. Without controlled and secure data sets, tests may provide misleading results. A decent test data strategy includes extracting a subset of production data representing real-world use cases while being small enough for fast execution. This subsetting should preserve relational consistency across dependent tables, which is particularly important in systems where data is tightly interrelated, like Oracle Financials or Supply Chain Management.
Data protection is another vital aspect because many Oracle apps store sensitive data. We recommend applying masking strategies to comply with data security regulations without sacrificing data realism. Implementing a reliable refresh and rollback mechanism is also a smart move.
Regular test script update
One of the key challenges of Oracle test automation is keeping test scripts up-to-date. Oracle frequently releases patches and updates that can modify UI components, database structures, or business logic. It is essential to keep test scripts updated with new system updates. Otherwise, they will fail.
The 3 stages of an effective test data strategy
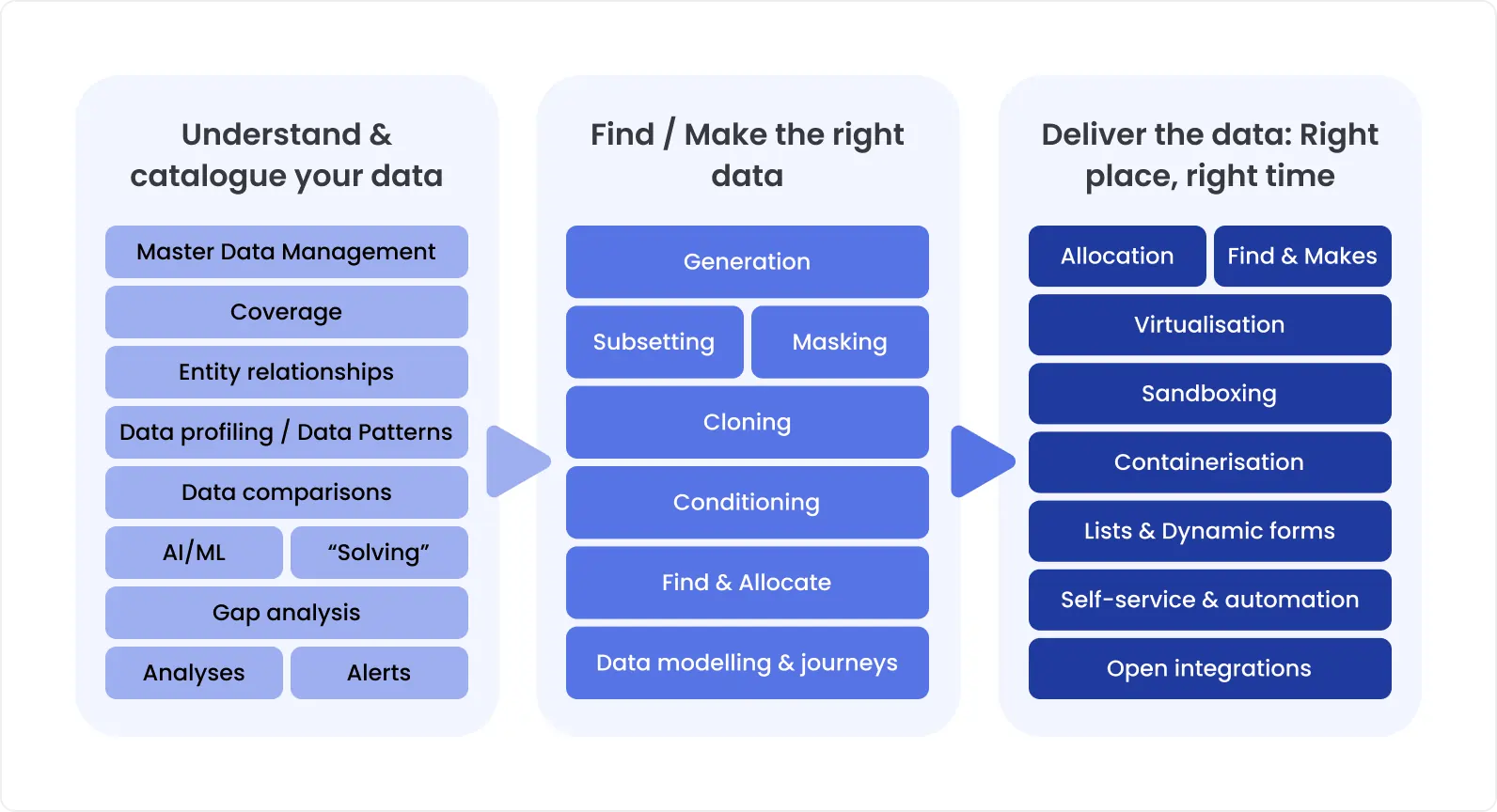
QA teams should familiarize themselves with Oracle release documentation to understand which modules or objects will be impacted by an update.
A test coverage matrix that maps automation scripts to specific modules, workflows, or functions helps them tweak all the corresponding tests.
Modular test script design also minimizes the maintenance burden. When a reusable function like login, item creation, or data entry is updated in one place, all dependent scripts automatically benefit from the change.
Step-by-step implementation of Oracle test automation
Oracle app automation is a strategic move that yields numerous benefits when implemented correctly. Below are key steps to take to succeed with this and ensure seamless work of Oracle apps, putting in minimal effort.
Step 1: Setting testing goals
First and foremost, it is strongly advised to align automation goals with real business risk and technical complexity. At this phase, you need to:
Define critical business flows across EBS modules, such as Procure-to-Pay, Order-to-Cash, Hire-to-Retire, etc.
Pinpoint customizations, integrations, and extensions that need to be thoroughly checked.
Identify error-prone areas of the app based on previous incidents and known pain points.
Decide on the exact scope of regression, compliance, and performance testing.
Step 2: Choose the right test automation tools
Oracle apps are developed with the help of Oracle Forms, OA Framework, and some HTML-based UIs, which usually aren't easily handled by the usual test automation tools. Before making your final tool choice, carefully evaluate the criteria listed below:
Support for Oracle Forms recording/playback or scripting.
Ability to handle dynamic elements in OAF and EBS self-service pages.
Allowing integration testing for APIs, workflows, and third-party connectors.
Compatibility with EBS environments.
Offering patch impact analysis or supporting Oracle’s Cumulative Patching Strategy.
Opkey, Tricentis Tosca, Leapwork, and Selenium are some suitable tools that can be used. Oracle's Automated Testing Suite also deserves your attention as an EBS-native tool that provides specialized accelerators and pre-built test scripts for automating both functional and regression testing, as well as load and performance testing of Oracle EBS applications.
Step 3: Building an efficient test automation solution
To effectively test Oracle apps, your test automation solution must be modular, Oracle-aware, and scalable.
Key elements you need to pay attention to:
Modular architecture: Organize scripts with reusable components across business processes.
Oracle-specific support: Ensure compatibility with Oracle Forms, OAF, ADF, and customized interfaces.
Data-driven testing: Insert external data into test scripts for more extensive coverage and flexible validations.
Environment control: Automate environment setup, health checks, and configuration tagging for complete consistency.
CI/CD integration: Integrate your automated tests into a CI/CD pipeline for scheduled or event-driven test runs.
Stability and logging: Build in retry logic, wait handling, and detailed logs with screenshots for the quick debugging of failures.
Step 4: Developing and executing test scripts
Create robust and maintainable test scripts that cover critical areas. Put your efforts into automating the tests that bring the highest value:
Regression tests that comprehensively check the operation of an Oracle app after updates.
UI tests that verify the layout of an Oracle app, including personalized and customized interfaces.
Performance tests that are executed to make sure an app can handle high workloads in an enterprise environment.
Integration tests that check if an Oracle app communicates seamlessly with external systems.
Database tests that verify data consistency, rollback scenarios, and transaction handling.
Security tests that ensure proper user access control and uncover potential vulnerabilities.
Step 5: Analyzing test results
After testing, you should study and analyze the results to reveal the root causes of issues and optimize the QA process if needed.
Implement execution logs and error messages for each test run to carry out root cause analysis and tie failures to specific customizations or environment issues.
Visualize trends – recurring failures, flaky test patterns, or regression hotspots – using tools like Allure, Grafana, or custom BI Publisher dashboards. This helps direct optimization efforts.
Create a test automation impact matrix linking automated test scripts to app modules, business flows, and customization areas. This way, you will be able to quickly prioritize relevant tests when a new Oracle patch or update is released.
Using Jenkins or GitLab CI, schedule critical test packs during patch windows or low-traffic periods. Automated smoke tests run right after patch deployment can catch critical failures early, before wider rollout.
Conclusion
Oracle apps power critical business functions, testing them isn’t optional. And with every customization, integration, system change, or Oracle update, new risks can surface. That’s why testing needs to be ongoing and handled by people who truly understand the Oracle ecosystem and have excellent test automation skills.
But establishing such a QA team in-house isn’t that easy. Fortunately, there are professional service providers like DeviQA that are ready to help.
With a wealth of hands-on experience, reliable tools, and Oracle-savvy testers, we’re ready to support your testing efforts.
Contact us and share your pain points with Oracle solutions testing, we’re equipped to handle them.
